DNA, Genes, and Chromosomes
The molecular basis of heredity and gene expression
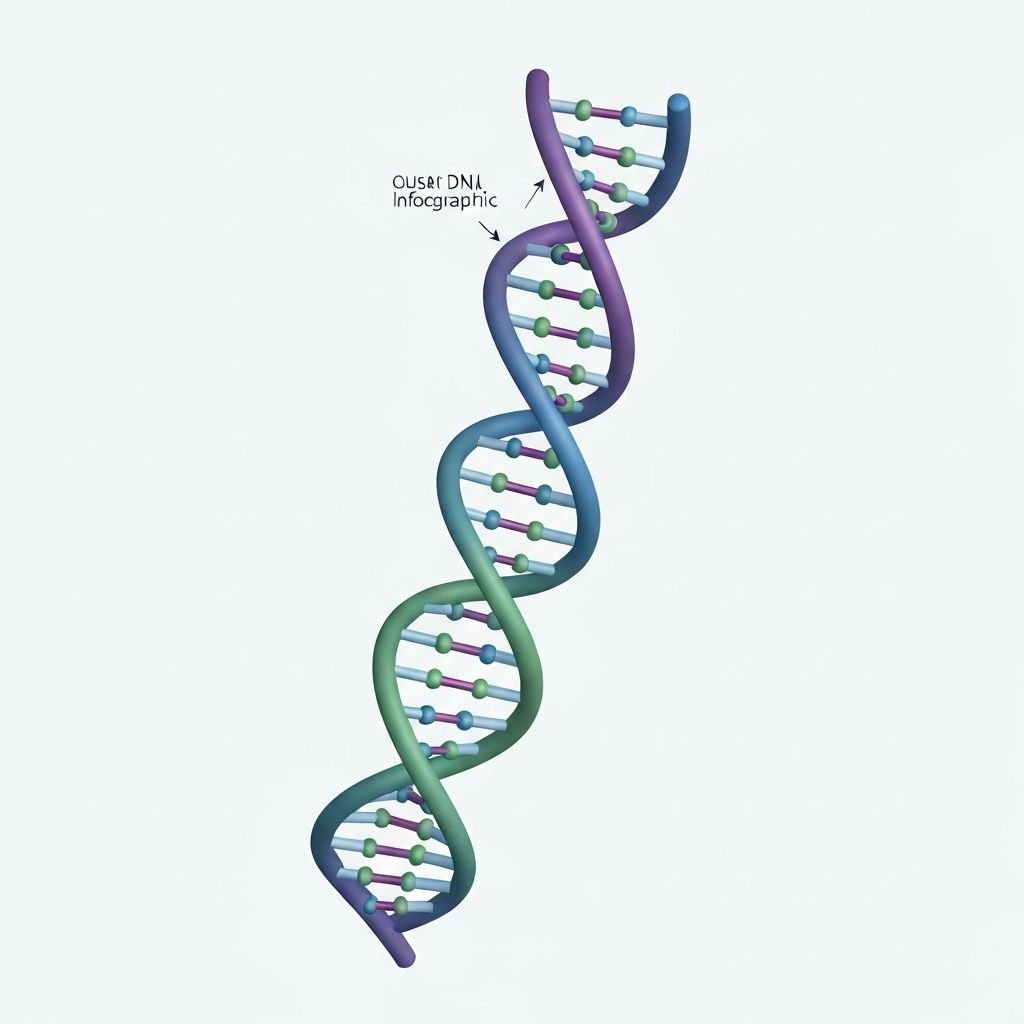
The Code of Life
DNA stores genetic information
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) is a double helix molecule that stores genetic information in all living organisms. It consists of two strands twisted around each other.
Sugar-Phosphate Backbone
The outer structure of DNA. Made of alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate groups
Nitrogenous Bases
Four types: Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Guanine (G), Cytosine (C). Form rungs of the DNA ladder
Base Pairing Rules
A pairs with T (2 hydrogen bonds), G pairs with C (3 hydrogen bonds). This is called complementary base pairing
Click a base above to see its complementary pair
Gene
A section of DNA that codes for a specific protein. Controls a particular characteristic (e.g., eye color, blood type)
Allele
Different versions of the same gene. For example, the eye color gene has alleles for blue, brown, green eyes
Chromosome
Long DNA molecule tightly coiled with proteins. Humans have 46 chromosomes (23 pairs) in body cells
Sex Chromosomes
23rd pair determines biological sex: XX = female, XY = male. Other 22 pairs are autosomes
Stage 1 of 4
Original DNA Double Helix
DNA exists as a double helix with two complementary strands held together by base pairs
Genes are expressed through a two-step process that converts DNA information into functional proteins.
1. Transcription (Nucleus)
DNA → mRNA (messenger RNA)
- DNA double helix unzips
- RNA polymerase enzyme reads DNA template strand
- Complementary mRNA strand is built (A→U, T→A, G→C, C→G)
- Note: RNA uses Uracil (U) instead of Thymine (T)
- mRNA leaves nucleus through nuclear pore
2. Translation (Ribosome)
mRNA → Protein
- mRNA binds to ribosome in cytoplasm
- Ribosome reads mRNA in triplets (codons)
- Each codon codes for specific amino acid
- tRNA (transfer RNA) brings correct amino acids
- Amino acids join together to form polypeptide chain (protein)
Step 1 of 4
DNA in Nucleus
DNA Template
Original DNA template strand contains genetic information
A mutation is a change in the DNA sequence. Mutations can occur spontaneously during DNA replication or be caused by environmental factors (radiation, chemicals).
Substitution
One base replaced by another
Insertion
Extra base added to sequence
Deletion
Base removed from sequence
Effects of Mutations
- Neutral: No effect on protein function
- Beneficial: Improves protein function (rare)
- Harmful: Disrupts protein function, may cause disease (e.g., sickle cell anemia)
Question: Given the DNA template strand TAC GCA TTA, determine the mRNA sequence and predict the amino acids
Step 1: Transcription (DNA → mRNA)
Apply base pairing rules (DNA to RNA): A→U, T→A, G→C, C→G
DNA template: TAC GCA TTA
mRNA: AUG CGU AAU
Step 2: Translation (mRNA → Amino Acids)
Read mRNA in triplets (codons) and use genetic code:
AUG → Methionine (Met) [START codon]
CGU → Arginine (Arg)
AAU → Asparagine (Asn)
Answer:
mRNA sequence: AUG CGU AAU
Amino acid sequence: Methionine - Arginine - Asparagine
Short form: Met-Arg-Asn