Sexual Reproduction in Humans
Reproductive systems, menstrual cycle, and human development
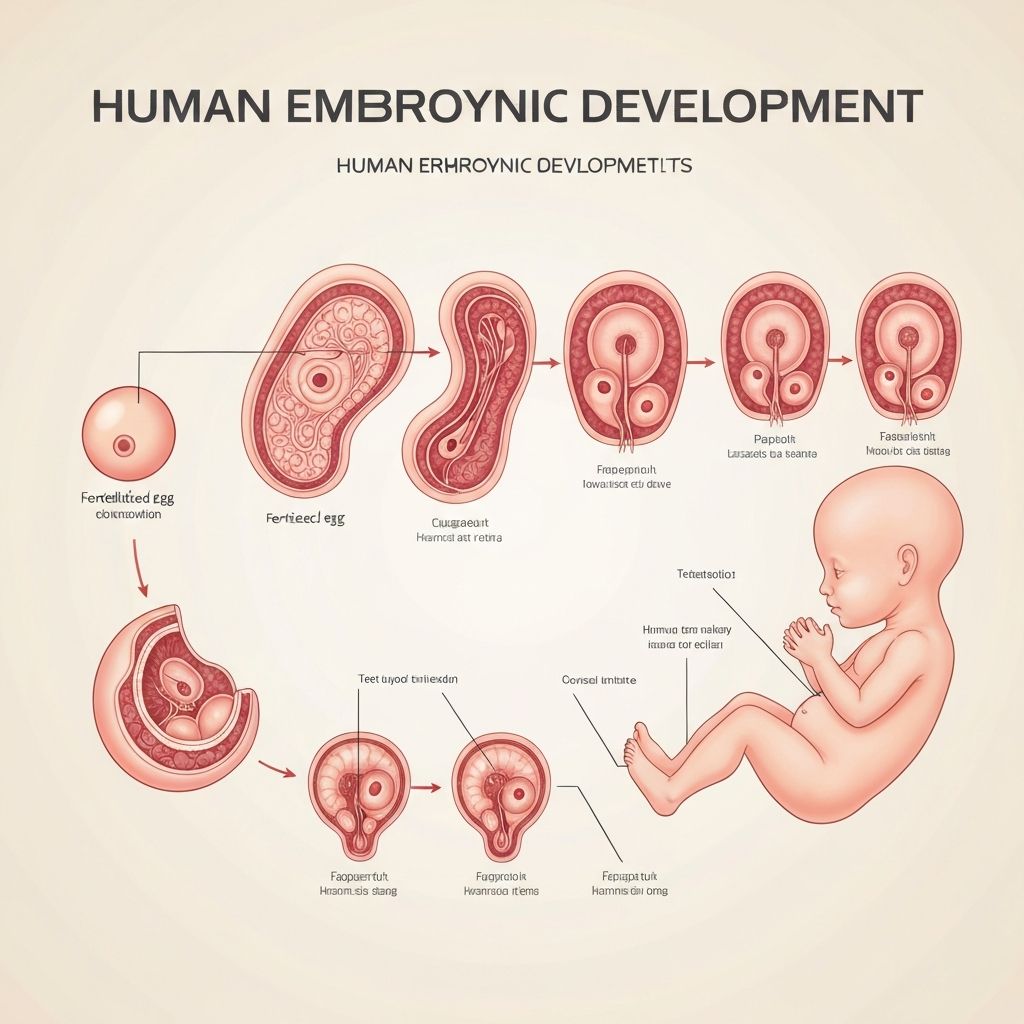
Human Life Begins
From gametes to birth
The male reproductive system produces and delivers sperm (male gametes) for fertilization.
Testes (Testicles)
Produce sperm and testosterone hormone. Located in scrotum (outside body) for temperature control
Epididymis
Coiled tube where sperm mature and are stored
Sperm Duct (Vas Deferens)
Carries sperm from testes to urethra
Urethra
Tube in penis that carries sperm (and urine) out of body
Prostate & Seminal Vesicles
Glands that add fluid to sperm, forming semen. Fluid provides nutrients and helps sperm swim
The female reproductive system produces eggs (female gametes) and provides an environment for fertilization and fetal development.
Ovaries
Produce eggs and hormones (estrogen, progesterone). Release one egg per month (ovulation)
Oviduct (Fallopian Tube)
Carries egg from ovary to uterus. Fertilization occurs here. Cilia help move egg along
Uterus (Womb)
Muscular organ where embryo implants and develops. Lining thickens monthly to prepare for pregnancy
Cervix
Ring of muscle at bottom of uterus. Opens during childbirth
Vagina
Muscular tube connecting uterus to outside. Birth canal during delivery
Menstruation
Uterus lining breaks down and is shed. Bleeding occurs.
Hormone Levels:
FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone)
From pituitary gland. Stimulates follicle and egg development
LH (Luteinizing Hormone)
From pituitary gland. Triggers ovulation on day 14
Estrogen
From ovary. Repairs uterus lining, inhibits FSH, stimulates LH
Progesterone
From corpus luteum. Maintains thick uterus lining for pregnancy
Sexual Intercourse
Sperm deposited in vagina, swim through cervix and uterus to oviduct
Fertilization
One sperm fuses with egg in oviduct. Nuclei combine to form zygote with 46 chromosomes
Cell Division
Zygote divides by mitosis as it travels to uterus, forming a ball of cells (embryo)
Implantation
Embryo embeds in thickened uterus lining (about 7 days after fertilization)
Fertilized egg (now a ball of cells called blastocyst) implants into thick uterus lining. Placenta begins to form.